Mitochondrial Dysfunction: Why Your Cellular Power Plants Are Failing
Do you crash every afternoon despite sleeping 8+ hours? Feel mentally foggy even after your third cup of coffee? Notice you're aging faster than your peers, despite eating well and exercising?
You might be dealing with mitochondrial dysfunction—a cellular energy crisis that's becoming epidemic in our modern world, yet most doctors never test for it or even consider it as a root cause.
Your mitochondria are the tiny power plants inside every cell, responsible for converting food and oxygen into usable energy (ATP). When they start failing, everything suffers: your energy, brain function, immune system, and even your ability to age gracefully.
Here's what's alarming: mitochondrial dysfunction is the hidden driver behind virtually every chronic disease, from diabetes and heart disease to Alzheimer's and cancer. Yet most people don't even know what mitochondria are, let alone how to protect them.
Understanding mitochondrial dysfunction could be the key to preventing chronic disease, restoring your energy, and adding healthy years to your life.
What is Mitochondrial Dysfunction?
Mitochondrial dysfunction occurs when your cellular power plants can't produce adequate energy to meet your body's demands. Think of it like having a failing electrical grid—some areas get power, others experience brownouts, and eventually entire systems start shutting down.
Inside each of your cells are hundreds to thousands of mitochondria, depending on the cell's energy needs. Your heart muscle cells contain about 5,000 mitochondria each, while your brain neurons can have up to 10,000. These microscopic factories work 24/7 to convert glucose, fats, and oxygen into ATP—the energy currency that powers every biological process in your body.[1]
When mitochondria become dysfunctional:
- ATP production drops dramatically
- Cellular repair and maintenance slow down
- Free radical damage increases
- Inflammation becomes chronic
- Organs and tissues can't function optimally
The most energy-demanding organs—your heart, brain, muscles, and immune system—are hit first and hardest when mitochondrial function declines.
The Modern Mitochondrial Crisis
Your mitochondria evolved over millions of years to function in a very different environment than today's world. Modern life presents unprecedented challenges that systematically damage these cellular power plants faster than your body can repair or replace them.
The frightening reality: Mitochondrial function declines significantly with age. Studies show skeletal muscle mitochondrial function can drop by 50% or more between young adulthood and older age, with similar declines occurring throughout the body.[2]
But this isn't just about aging. Environmental toxins, chronic stress, processed foods, blue light exposure, and sedentary lifestyles are accelerating mitochondrial damage at unprecedented rates. Many people in their 30s and 40s now show mitochondrial dysfunction patterns that previous generations didn't experience until their 70s.
Factors accelerating mitochondrial dysfunction:
- Chronic stress and elevated cortisol
- Environmental toxins and heavy metals
- Processed foods lacking essential cofactors
- Blue light exposure disrupting circadian rhythms
- Sedentary lifestyle or excessive intense exercise
- Certain medications (statins, antibiotics, NSAIDs)
- Poor sleep quality and insufficient recovery
This systematic assault on your mitochondria explains why chronic disease rates are skyrocketing despite advances in medical technology.
9 Warning Signs of Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Mitochondrial dysfunction often develops gradually, with symptoms that are easy to dismiss as "normal aging" or stress. Here are the key warning signs your cellular power plants are struggling:
1. Chronic Fatigue That Rest Doesn't Fix
The symptom: Persistent exhaustion despite adequate sleep, or feeling tired shortly after waking up.
What's happening: When mitochondria can't produce sufficient ATP, your cells literally run out of fuel. This isn't the kind of tiredness that improves with rest—it's cellular energy starvation.
Why it matters: Unlike fatigue from overwork or poor sleep, mitochondrial fatigue doesn't improve with lifestyle changes alone. It requires addressing the underlying cellular energy crisis.
2. The 3pm Energy Crash (Even After Good Sleep)
The symptom: Predictable afternoon energy crashes that leave you reaching for caffeine or sugar.
What's happening: Damaged mitochondria can maintain energy production for 6-8 hours after waking, but then hit their limit. When cellular energy drops, your body craves quick fuel sources.
Why it matters: This pattern indicates your mitochondria are working at maximum capacity just to get through half a day—a clear sign of dysfunction.
3. Brain Fog and Mental Fatigue
The symptom: Difficulty concentrating, forgetfulness, feeling mentally "cloudy" or underwater.
What's happening: Your brain consumes approximately 20% of your body's total energy despite being only 2% of your body weight, making it extremely vulnerable to mitochondrial dysfunction. When mitochondria fail, brain function suffers first because neurons have such high energy demands.[3]
Why it matters: Persistent brain fog, especially when combined with fatigue, often indicates mitochondrial dysfunction rather than stress or aging alone. People experiencing these symptoms alongside other nutrient deficiencies often have B12 deficiency symptoms that compound the problem.
4. Exercise Intolerance and Poor Recovery
The symptom: Getting winded easily, feeling exhausted after light exercise, or taking days to recover from workouts that used to be manageable.
What's happening: Exercise requires mitochondria to rapidly increase energy production. When they're dysfunctional, even moderate activity becomes overwhelming, and recovery takes much longer.
Why it matters: This creates a vicious cycle—you need exercise to stimulate healthy mitochondria, but you can't exercise effectively when mitochondria are failing.
5. Temperature Regulation Problems
The symptom: Feeling cold when others are comfortable, having consistently cold hands and feet, or difficulty warming up even with layers.
What's happening: Mitochondria generate heat as a byproduct of energy production. When they're not functioning properly, your body struggles to maintain optimal temperature.
Why it matters: Poor temperature regulation often indicates that mitochondria aren't producing adequate energy or are producing energy inefficiently.
6. Frequent Infections and Slow Healing
The symptom: Catching every bug that goes around, taking weeks to recover from minor illnesses, or cuts and bruises healing slowly.
What's happening: Immune cells have more mitochondria than almost any other cell type because fighting infections requires massive energy. When mitochondria are compromised, immune function suffers.[4]
Why it matters: A weakened immune system increases risk for autoimmune diseases, chronic infections, and even cancer.
7. Mood Issues and Anxiety
The symptom: Unexplained anxiety, depression that doesn't respond to traditional treatments, or mood swings that correlate with energy levels.
What's happening: Neurotransmitter production (serotonin, dopamine, GABA) requires enormous amounts of cellular energy. When mitochondria can't keep up, mood regulation suffers.
Why it matters: Many cases of treatment-resistant depression and anxiety may actually be mitochondrial dysfunction in disguise.
8. Accelerated Aging and Poor Skin Health
The symptom: Looking older than your chronological age, skin that appears dull or aged, poor wound healing, or premature graying.
What's happening: All cellular repair and regeneration processes depend on mitochondrial energy. When ATP production declines, cellular maintenance slows dramatically.
Why it matters: Visible aging acceleration indicates that cellular repair processes throughout your body are compromised, increasing disease risk.
9. Multiple Chemical Sensitivities
The symptom: Increased sensitivity to perfumes, cleaning products, certain foods, or environmental toxins that didn't bother you before.
What's happening: Detoxification requires significant cellular energy. When mitochondria are struggling, your body can't process toxins effectively, leading to increased sensitivities.
Why it matters: Chemical sensitivities often develop as mitochondrial function declines, creating a cycle where toxin exposure further damages already compromised cellular energy production.
The Disease Connection Most Doctors Miss
Here's what mainstream medicine doesn't understand: mitochondrial dysfunction isn't just making you tired—it's the root cause driving virtually every chronic disease.
Your doctor sees diabetes, heart disease, Alzheimer's, and autoimmune conditions as separate diseases requiring different treatments. But they're all manifestations of the same underlying problem: cellular energy failure in different organ systems.
Type 2 Diabetes: Muscle Mitochondrial Failure
What really happens: Your muscle cells contain thousands of mitochondria that need energy to properly absorb glucose. When muscle mitochondria become dysfunctional, they can't utilize glucose effectively, leading to elevated blood sugar.
The conventional approach: Manage blood sugar with medications
The mitochondrial approach: Restore muscle cell energy production
Heart Disease: Cardiac Mitochondrial Burnout
What really happens: Your heart beats 100,000+ times daily, requiring more mitochondria than any other organ. When cardiac mitochondria fail, pumping efficiency drops, leading to high blood pressure and eventual heart failure.
The conventional approach: Blood pressure medications and procedures
The mitochondrial approach: Restore cardiac cellular energy production
Alzheimer's Disease: Brain Mitochondrial Collapse
What really happens: Brain tissue has enormous energy demands. When brain mitochondria fail, neurons can't maintain function, clear waste products, or form new memories.
The conventional approach: Manage symptoms and delay progression
The mitochondrial approach: Restore brain cellular energy and prevent decline
Autoimmune Diseases: Immune Cell Energy Crisis
What really happens: Immune cells require massive amounts of energy to function properly. When immune mitochondria malfunction, the immune system becomes confused and overactive, attacking your own tissues.
The conventional approach: Suppress immune function with drugs
The mitochondrial approach: Restore immune cell energy production
Understanding this connection changes everything: instead of treating multiple diseases separately, you can address the root cause driving all of them.
What Causes Mitochondrial Dysfunction?
Mitochondrial dysfunction rarely has a single cause. Instead, it's usually the result of multiple factors overwhelming your cellular repair capacity:
Chronic Stress and Poor Sleep
Elevated cortisol directly damages mitochondrial membranes and interferes with mitochondrial DNA repair. Poor sleep prevents the cellular cleanup and repair processes that maintain healthy mitochondria.
Nutrient Deficiencies
Mitochondria require specific nutrients to function: magnesium, B vitamins, CoQ10, iron, and others. Modern diets often lack these cofactors, while soil depletion reduces nutrient density in foods.
Environmental Toxins
Heavy metals, pesticides, air pollution, and chemicals accumulate in mitochondrial membranes, interfering with energy production and causing direct DNA damage.
Processed Foods and Sugar
High-fructose corn syrup, trans fats, and excess refined sugar create inflammatory byproducts that damage mitochondria while providing none of the nutrients needed for cellular repair.
Sedentary Lifestyle
Mitochondria follow a "use it or lose it" principle. Prolonged inactivity leads to mitochondrial loss, while excessive intense exercise without adequate recovery can create oxidative damage.
Aging
Natural aging reduces mitochondrial biogenesis (the creation of new mitochondria) while increasing mitochondrial DNA damage and dysfunction.
Medications
Certain drugs, particularly statins, antibiotics, and NSAIDs, can interfere with mitochondrial function or deplete essential cofactors like CoQ10.
How to Restore Mitochondrial Function
The good news: mitochondria have remarkable regenerative capacity when given proper support. Here's how to rebuild your cellular power plants:
Provide Essential Mitochondrial Nutrients
PQQ (Pyrroloquinoline Quinone): The only known compound that stimulates growth of new mitochondria. Studies show 10-20mg daily can increase mitochondrial number by 20-30%.[5]
CoQ10: Essential for the electron transport chain that produces ATP. Age-related decline requires supplementation with 100-300mg daily for restoration. Learn more about CoQ10 benefits for energy and heart health.
Magnesium: Required for over 300 enzymatic reactions including all steps of ATP production. Most people need 400-600mg daily in bioavailable forms like glycinate. Many people showing mitochondrial dysfunction symptoms also have magnesium deficiency symptoms.
B Vitamins: Essential cofactors for energy production, particularly B1, B2, B3, B5, and B12 in their active forms. For people with genetic variations, understanding MTHFR gene mutation symptoms is crucial for proper B vitamin supplementation.
Taurine: Stabilizes mitochondrial membranes and is essential for proper calcium handling within mitochondria.
Support Mitochondrial Biogenesis
Cold exposure: Brief cold showers or ice baths stimulate new mitochondrial growth
High-intensity interval training: Short bursts of intense exercise followed by recovery
Intermittent fasting: Gives mitochondria time to repair and regenerate
Red light therapy: Specific wavelengths can enhance mitochondrial function
Reduce Mitochondrial Damage
Manage stress: Chronic stress is one of the biggest mitochondrial destroyers
Optimize sleep: 7-9 hours of quality sleep allows mitochondrial repair
Limit toxin exposure: Reduce environmental toxins when possible
Anti-inflammatory diet: Focus on whole foods rich in antioxidants
Address Root Causes
Fix nutrient deficiencies: Comprehensive testing and targeted supplementation. Most people taking basic vitamins are still deficient because most multivitamins are worthless and don't contain therapeutic doses of mitochondrial support compounds.
Improve gut health: Poor digestion reduces nutrient absorption
Balance hormones: Thyroid and sex hormone optimization supports mitochondrial function
Treat infections: Chronic infections drain mitochondrial energy
The Mitochondrial Health Investment
Quality mitochondrial restoration isn't cheap, but consider what you're investing in:
- Restored cellular energy and mental clarity
- Enhanced resilience to stress and illness
- Slower aging at the cellular level
- Potential prevention of multiple chronic diseases
- Improved quality of life for decades
The cost of not addressing mitochondrial dysfunction—decades of fatigue, accelerated aging, and chronic disease treatments—is far higher than investing in cellular health now.
Your Cellular Power Plants Need Support
Your mitochondria have been working tirelessly for decades, powering every heartbeat, every thought, every cellular repair process. They've adapted as best they can to the challenges of modern life, but they need support.
Mitochondrial dysfunction isn't inevitable aging—it's a preventable and reversible condition when you understand what your cellular power plants actually need.
The compounds that can restore mitochondrial function exist, backed by research, but most people never learn about them.
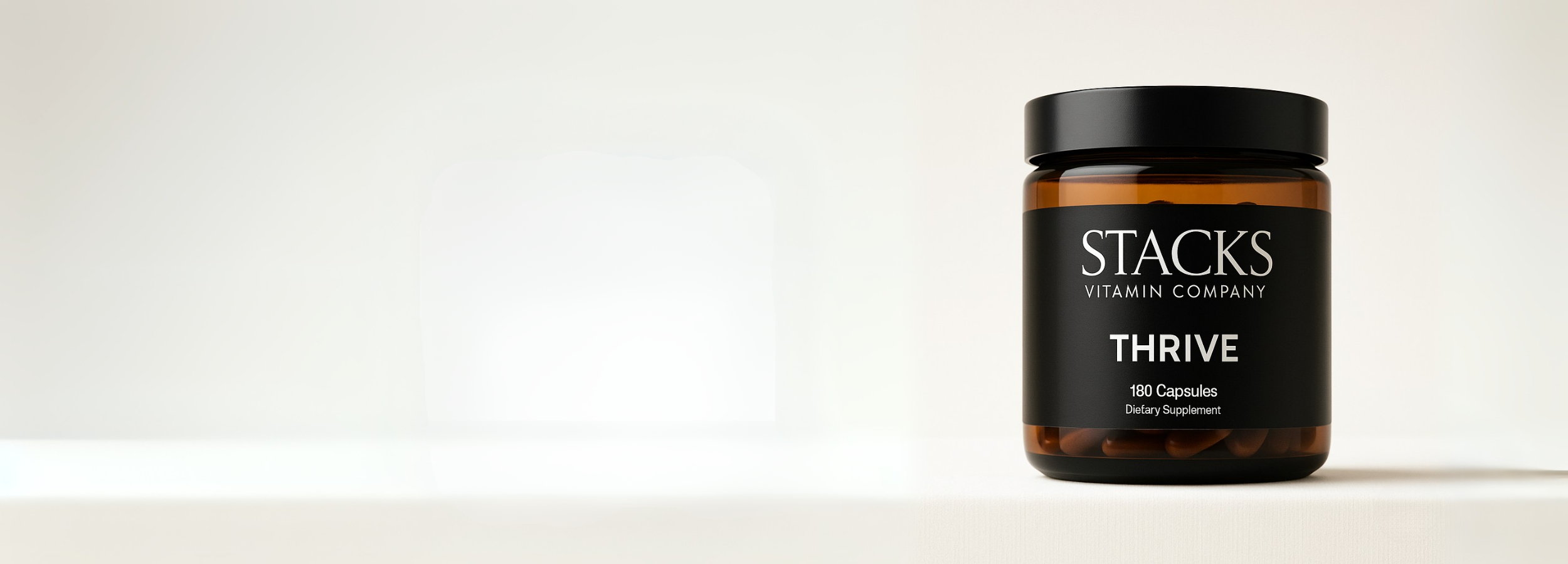
Restore Your Mitochondrial Function with THRIVE
Our premium multivitamin, THRIVE, contains 10mg of PQQ for mitochondrial biogenesis, 200mg of CoQ10 for energy production, and 400mg of magnesium glycinate for enzymatic function—therapeutic doses that support cellular energy restoration and mitochondrial health.
Unlike typical multivitamins that contain little to no mitochondrial support compounds, THRIVE provides meaningful amounts of these crucial nutrients in optimally absorbed forms alongside synergistic compounds like B vitamins, taurine, and adaptogens that work together to optimize cellular function.
THRIVE delivers comprehensive mitochondrial support with therapeutic doses of PQQ, CoQ10, and essential cofactors that most people are deficient in due to age, stress, and modern lifestyle factors.
Learn more about THRIVE Premium Multivitamin →
Ready to experience what optimal cellular energy feels like? Discover how Stacks Vitamin Company provides the therapeutic nutrients your mitochondria need to thrive.
Note: This article is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a physician before taking any supplement. These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
References: